¶ 竖直四子棋
¶ 题目描述
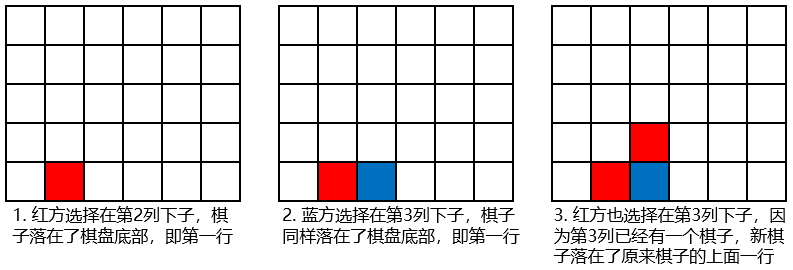
竖直四子棋的棋盘是竖立起来的,双方轮流选择棋盘的一列下子,
棋子因重力落到棋盘底部或者其他棋子之上,当一列的棋子放满时,无法再在这列上下子。
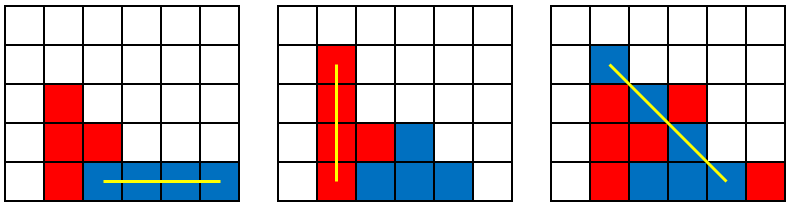
一方的4个棋子横、竖或者斜方向连成一线时获胜。
现给定一个棋盘和红蓝对弈双方的下子步骤,判断红方或蓝方是否在某一步获胜。
下面以一个6x5的棋盘图示说明落子过程:
下面给出横、竖和斜方向四子连线的图示:
¶ 输入描述
输入为2行,第一行指定棋盘的宽和高,为空格分隔的两个数字;
第二行依次间隔指定红蓝双方的落子步骤,第1步为红方的落子,第2步为蓝方的落子,第3步为红方的落子,以此类推。
步骤由空格分隔的一组数字表示,每个数字为落子的列的编号(最左边的列编号为1,往右递增)。用例保证数字均为32位有符号数。
¶ 输出描述
如果落子过程中红方获胜,输出 N,red ;
如果落子过程中蓝方获胜,输出 N,blue ;
如果出现非法的落子步骤,输出 N,error。
N为落子步骤的序号,从1开始。如果双方都没有获胜,输出 0,draw 。
非法落子步骤有两种,一是列的编号超过棋盘范围,二是在一个已经落满子的列上落子。
N和单词red、blue、draw、error之间是英文逗号连接。
¶ 示例一
¶ 输入
5 5
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
¶ 输出
7,red
¶ 说明
在第7步,红方在第4列落下一子后,红方的四个子在第一行连成一线,故红方获胜,输出 7,red
¶ 示例二
¶ 输入
5 5
0 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
¶ 输出
1,error
¶ 说明
第1步的列序号为0,超出有效列编号的范围,故输出 1,error
¶ 参考解题 Java
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Author: Amos
* E-mail: amos@amoscloud.com
* Date: 2022/9/17
* Time: 16:40
* Description:
*/
public class Main0134 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in)) {
String[] nums = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
int m = Integer.parseInt(nums[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(nums[1]);
String[] strings = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
solution(m, n, strings);
}
}
private static void solution(int m, int n, String[] strings) {
int[][] ints = new int[n][m];
boolean isOver = false;
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
int index = -1;
int color = 1;
int num = Integer.parseInt(strings[i]);
if (num <= 0 || num > m || ints[0][num - 1] != 0) {
isOver = true;
System.out.println(i + 1 + ",error");
break;
}
if (i % 2 != 0) { //偶数下标为red,用1表示
color = 2; //奇数下标为blue,用2表示
}
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (ints[j][num - 1] == 0) {
index = j; //此时棋子横坐标为j,纵坐标为num-1
ints[j][num - 1] = color;
break;
}
}
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println(i + 1 + ",error");
isOver = true;
break;
}
if (i >= 6 && isSuccess(ints, index, num - 1)) { //第七个棋子才开始符合四棋子的要求
if (color == 1) {
System.out.println(i + 1 + ",red");
isOver = true;
break;
} else {
System.out.println(i + 1 + ",blue");
isOver = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!isOver) {
System.out.println("0,draw");
}
}
public static boolean isSuccess(int[][] ints, int x, int y) {
int h = ints.length; //数组有h行
int l = ints[0].length; //数组有l列
int count = 0; //统计相同的棋子(3即可)
int jishu = 3; //四个棋子只要统计三次
if (x < h - 3) { //是否满足棋子纵向四棋子
int a = x;
while ((jishu != 0) && ints[a][y] == ints[++a][y]) {
count++;
jishu--;
}
if (count == 3) {
return true;
}
count = 0;
jishu = 3;
}
if (y >= 3) { //是否满足棋子左边横向四棋子
int b = y;
while ((jishu != 0) && ints[x][b] == ints[x][--b]) {
count++;
jishu--;
}
if (count == 3) {
return true;
}
count = 0;
jishu = 3;
}
if (y < l - 3) { //是否满足棋子右边横向四棋子
int b = y;
while ((jishu != 0) && ints[x][b] == ints[x][++b]) {
count++;
jishu--;
}
if (count == 3) {
return true;
}
count = 0;
jishu = 3;
}
if (x < h - 3 && y >= 3) { //是否满足左边斜向四棋子
int a = x;
int b = y;
while ((jishu != 0) && ints[a][b] == ints[++a][--b]) {
count++;
jishu--;
}
if (count == 3) {
return true;
}
count = 0;
jishu = 3;
}
if (x < h - 3 && y < l - 3) { //是否满足右边斜向四棋子
int a = x;
int b = y;
while ((jishu != 0) && ints[a][b] == ints[++a][++b]) {
count++;
jishu--;
}
return count == 3;
}
return false;
}
}